TOKYO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Kewpie Corporation (“Kewpie”) (TOKYO:2809) has confirmed that adding mayonnaise or emulsified dressings improves the ease of eating of foods such as vegetables that the elderly find difficult to eat. This was found out through joint research with Professor Yukie Yanagisawa et al of Wayo Women's University. The results of this research were announced at the 35th General Meeting of Japanese Society for Mastication Science and Health Promotion, held on September 14 and 15, 2024.
1. Background to the research
Declines in ability to eat (bite strength and swallowing ability) not only makes it difficult to eat meals day-to-day, but can also result in food entering the trachea and leading to aspiration pneumonia. Eating ability declining with age is considered a social issue in Japan, with the highest proportion of elderly in the world.*1 Rapidly aging populations are expected on a global basis as well,*2 and international efforts to standardize dysphagia foods have begun.*3
In Japan, in addition to the use of foods designed to be easy to eat, called “universal design foods”, there are proposals, especially at the front lines of home care guidance, to use mayonnaise or emulsified dressings (“emulsified condiments”) that most households would have as a way to make daily food easier to eat.
2. Purpose of the research
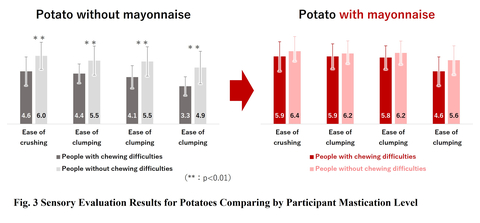
It was conjectured that mixing emulsified condiments with hard-to-eat foodstuffs such as vegetables would help them clump together and provide smoothness, leading to improvements to their ease of eating. This research aimed at scientifically understanding the improved ease of eating through the use of these emulsified condiments. To that end, a sensory evaluation was carried out using middle-aged and elderly participants.
3. Outline of the results
In all assessed foods, the addition of emulsified condiments was shown to significantly improve the ease of eating. In particular, participants with declining bite strength felt the results more strongly than those of normal strength, showing it had the possibility of being effective.
In this research, we confirmed the significant effects of emulsified condiments on the ease of eating through a sensory evaluation by middle-aged and elderly participants, the generations starting to worry about their declining ability to eat. In future, we shall work on further understanding this mechanism by also carrying out verification using objective measures such as measuring myoelectric potential during swallowing. Emulsified condiments contain oils, so are also good to combat the lowered nutritional intake of the elderly. Building on the knowledge gained this time, we shall provide useful information for households or elderly care facilities such as suggesting menus for those concerned about frailty or private-sector carers. Kewpie will continue to work on research aimed at solving issues related to food, contributing to the enrichment of dietary life for everyone.
*1. Cabinet Office, 2022 White Paper on Aging Society
*2. UN, World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision
*3. International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative
Research Outline (Experiment description and Results)
News Release
About Kewpie Corporation
Founded in 1919, Kewpie Corporation is a leading food manufacturer headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. Known for its mayonnaise, which will celebrate its 100th anniversary in 2025 in Japan, Kewpie is committed to contributing to global food culture and health through "great taste, empathy, and uniqueness". Operating globally with production facilities and sales offices in major international markets, Kewpie is dedicated to enriching people's lives through food.
For more information, visit Kewpie's official website.
https://www.kewpie.com/en/